Java TreeMap类
TreeMap继承了NavigableMap,而NavigableMap继承自SortedMap,为SortedMap添加了搜索选项,NavigableMap有几种方法,分别是不同的比较要求:floorKey是小于等于,ceilingKey是大于等于,lowerKey是小于,higherKey是大于。
构造函数
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeMap中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。 TreeMap() // 创建的TreeMap包含Map TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> copyFrom) // 指定Tree的比较器 TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) // 创建的TreeSet包含copyFrom TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> copyFrom)
属性
//比较器,因为TreeMap是有序的,通过comparator接口我们可以对TreeMap的内部排序进行精密的控制 private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; //TreeMap红-黑节点,为TreeMap的内部类 private transient Entry<K,V> root = null; //容器大小 private transient int size = 0; //TreeMap修改次数 private transient int modCount = 0; //红黑树的节点颜色--红色 private static final boolean RED = false; //红黑树的节点颜色--黑色 private static final boolean BLACK = true;
方法
Entry<K, V> ceilingEntry(K key) K ceilingKey(K key) void clear() Object clone() Comparator<? super K> comparator() boolean containsKey(Object key) NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() Entry<K, V> firstEntry() K firstKey() Entry<K, V> floorEntry(K key) K floorKey(K key) V get(Object key) NavigableMap<K, V> headMap(K to, boolean inclusive) SortedMap<K, V> headMap(K toExclusive) Entry<K, V> higherEntry(K key) K higherKey(K key) boolean isEmpty() Set<K> keySet() Entry<K, V> lastEntry() K lastKey() Entry<K, V> lowerEntry(K key) K lowerKey(K key) NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry() Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry() V put(K key, V value) V remove(Object key) int size() SortedMap<K, V> subMap(K fromInclusive, K toExclusive) NavigableMap<K, V> subMap(K from, boolean fromInclusive, K to, boolean toInclusive) NavigableMap<K, V> tailMap(K from, boolean inclusive) SortedMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromInclusive)
继承关系
java.lang.Object
java.util.AbstractMap<K, V>
java.util.TreeMap<K, V>
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
TreeMap与Map关系
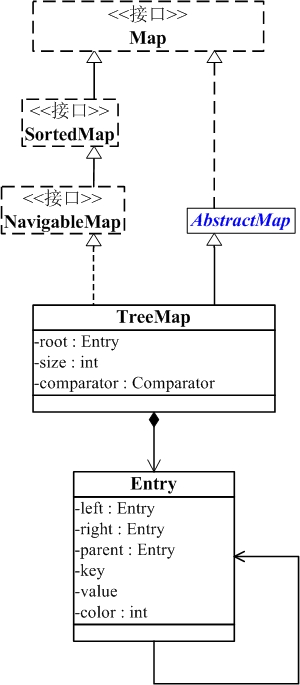
从图中可以看出:
(01) TreeMap实现继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了NavigableMap接口。
(02) TreeMap的本质是R-B Tree(红黑树),它包含几个重要的成员变量: root, size, comparator。
例子
/**
* @desc TreeMap测试程序
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试常用的API
testTreeMapOridinaryAPIs();
// 测试TreeMap的导航函数
//testNavigableMapAPIs();
// 测试TreeMap的子Map函数
//testSubMapAPIs();
}
/**
* 测试常用的API
*/
private static void testTreeMapOridinaryAPIs() {
// 初始化随机种子
Random r = new Random();
// 新建TreeMap
TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap();
// 添加操作
tmap.put("one", r.nextInt(10));
tmap.put("two", r.nextInt(10));
tmap.put("three", r.nextInt(10));
System.out.printf("\n ---- testTreeMapOridinaryAPIs ----\n");
// 打印出TreeMap
System.out.printf("%s\n",tmap );
// 通过Iterator遍历key-value
Iterator iter = tmap.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
System.out.printf("next : %s - %s\n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// TreeMap的键值对个数
System.out.printf("size: %s\n", tmap.size());
// containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
System.out.printf("contains key two : %s\n",tmap.containsKey("two"));
System.out.printf("contains key five : %s\n",tmap.containsKey("five"));
// containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
System.out.printf("contains value 0 : %s\n",tmap.containsValue(new Integer(0)));
// remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
tmap.remove("three");
System.out.printf("tmap:%s\n",tmap );
// clear() : 清空TreeMap
tmap.clear();
// isEmpty() : TreeMap是否为空
System.out.printf("%s\n", (tmap.isEmpty()?"tmap is empty":"tmap is not empty") );
}
/**
* 测试TreeMap的子Map函数
*/
public static void testSubMapAPIs() {
// 新建TreeMap
TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap();
// 添加“键值对”
tmap.put("a", 101);
tmap.put("b", 102);
tmap.put("c", 103);
tmap.put("d", 104);
tmap.put("e", 105);
System.out.printf("\n ---- testSubMapAPIs ----\n");
// 打印出TreeMap
System.out.printf("tmap:\n\t%s\n", tmap);
// 测试 headMap(K toKey)
System.out.printf("tmap.headMap(\"c\"):\n\t%s\n", tmap.headMap("c"));
// 测试 headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive)
System.out.printf("tmap.headMap(\"c\", true):\n\t%s\n", tmap.headMap("c", true));
System.out.printf("tmap.headMap(\"c\", false):\n\t%s\n", tmap.headMap("c", false));
// 测试 tailMap(K fromKey)
System.out.printf("tmap.tailMap(\"c\"):\n\t%s\n", tmap.tailMap("c"));
// 测试 tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive)
System.out.printf("tmap.tailMap(\"c\", true):\n\t%s\n", tmap.tailMap("c", true));
System.out.printf("tmap.tailMap(\"c\", false):\n\t%s\n", tmap.tailMap("c", false));
// 测试 subMap(K fromKey, K toKey)
System.out.printf("tmap.subMap(\"a\", \"c\"):\n\t%s\n", tmap.subMap("a", "c"));
// 测试
System.out.printf("tmap.subMap(\"a\", true, \"c\", true):\n\t%s\n",
tmap.subMap("a", true, "c", true));
System.out.printf("tmap.subMap(\"a\", true, \"c\", false):\n\t%s\n",
tmap.subMap("a", true, "c", false));
System.out.printf("tmap.subMap(\"a\", false, \"c\", true):\n\t%s\n",
tmap.subMap("a", false, "c", true));
System.out.printf("tmap.subMap(\"a\", false, \"c\", false):\n\t%s\n",
tmap.subMap("a", false, "c", false));
// 测试 navigableKeySet()
System.out.printf("tmap.navigableKeySet():\n\t%s\n", tmap.navigableKeySet());
// 测试 descendingKeySet()
System.out.printf("tmap.descendingKeySet():\n\t%s\n", tmap.descendingKeySet());
}
/**
* 测试TreeMap的导航函数
*/
public static void testNavigableMapAPIs() {
// 新建TreeMap
NavigableMap nav = new TreeMap();
// 添加“键值对”
nav.put("aaa", 111);
nav.put("bbb", 222);
nav.put("eee", 333);
nav.put("ccc", 555);
nav.put("ddd", 444);
System.out.printf("\n ---- testNavigableMapAPIs ----\n");
// 打印出TreeMap
System.out.printf("Whole list:%s%n", nav);
// 获取第一个key、第一个Entry
System.out.printf("First key: %s\tFirst entry: %s%n",nav.firstKey(), nav.firstEntry());
// 获取最后一个key、最后一个Entry
System.out.printf("Last key: %s\tLast entry: %s%n",nav.lastKey(), nav.lastEntry());
// 获取“小于/等于bbb”的最大键值对
System.out.printf("Key floor before bbb: %s%n",nav.floorKey("bbb"));
// 获取“小于bbb”的最大键值对
System.out.printf("Key lower before bbb: %s%n", nav.lowerKey("bbb"));
// 获取“大于/等于bbb”的最小键值对
System.out.printf("Key ceiling after ccc: %s%n",nav.ceilingKey("ccc"));
// 获取“大于bbb”的最小键值对
System.out.printf("Key higher after ccc: %s%n\n",nav.higherKey("ccc"));
}
}
运行结果:
{one=8, three=4, two=2}
next : one - 8
next : three - 4
next : two - 2
size: 3
contains key two : true
contains key five : false
contains value 0 : false
tmap:{one=8, two=2}
tmap is empty
总结
1. TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
2. TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
3. TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
4. TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
5. TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
6. TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
7. TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
8. TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
版权声明:本文为JAVASCHOOL原创文章,未经本站允许不得转载。

